DNS and Load Balancing
DNS server can work as a load balancer, as multiple IP addresses can be bound to a single DNS server
GSLB provides more functionalities (load balancing algorithm, health check, failover, etc).
Global Server Load Balancing
GSLB distributes traffic across multiple servers in different regions. It prevents the local and regional load balancers and the workloads behind from being overloaded.
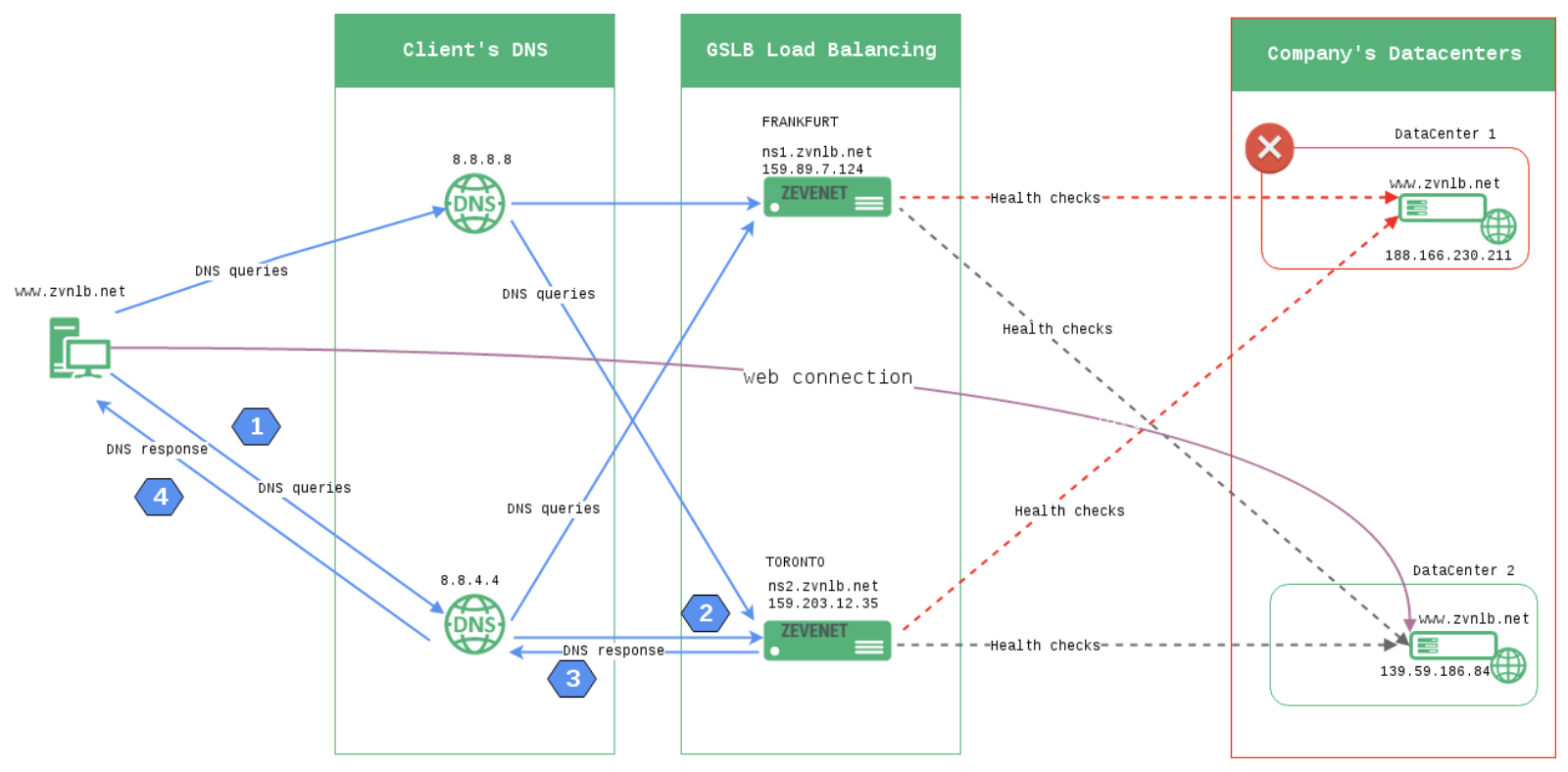
When a client sends a DNS request, GSLB intercepts the request to determine which IP address to return. This determination depends on a set of policies set (health, location, latency, etc)
- Client sends a DNS query to local DNS to access www.example.com.
- GSLB intercepts the DNS query from the local DNS.
- Based on the policy and the information GSLB has, GSLB returns the suitable IP address to the local DNS.
- The local DNS gives response to the client
GSLB Healthcheck
GSLB administrator can set a healthcheck method (TCP, HTTPS, HTTP, etc) to regularly check whether the servers are healthy. For example, a HTTPS endpoint (/management/health) can be used to check whether a server is healthy.